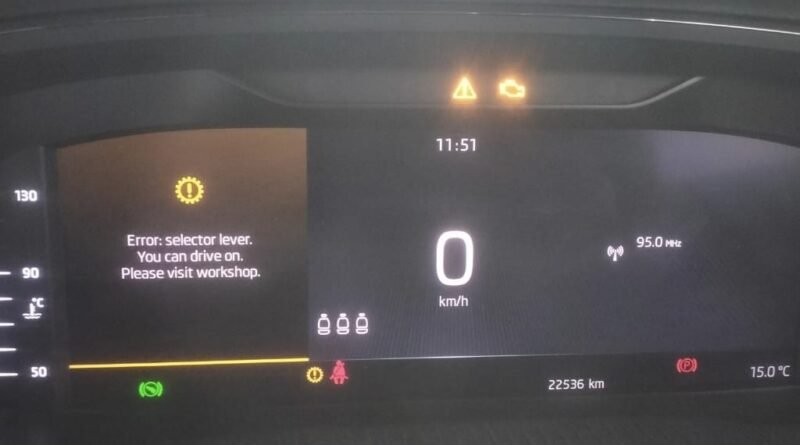
Understanding OBD Codes P175D P175E and P177B – Clutch 1 Issues
OBD Codes P175D P175E and P177B: Modern vehicles equipped with automated transmissions, including dual-clutch and automated manual systems, rely on precise control of clutch operations for smooth performance. When faults occur in these systems, the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system generates specific Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). Codes P175D, P175E, and P177B are related to Clutch 1 in the transmission system. This article explores these codes, their symptoms, causes, and solutions.
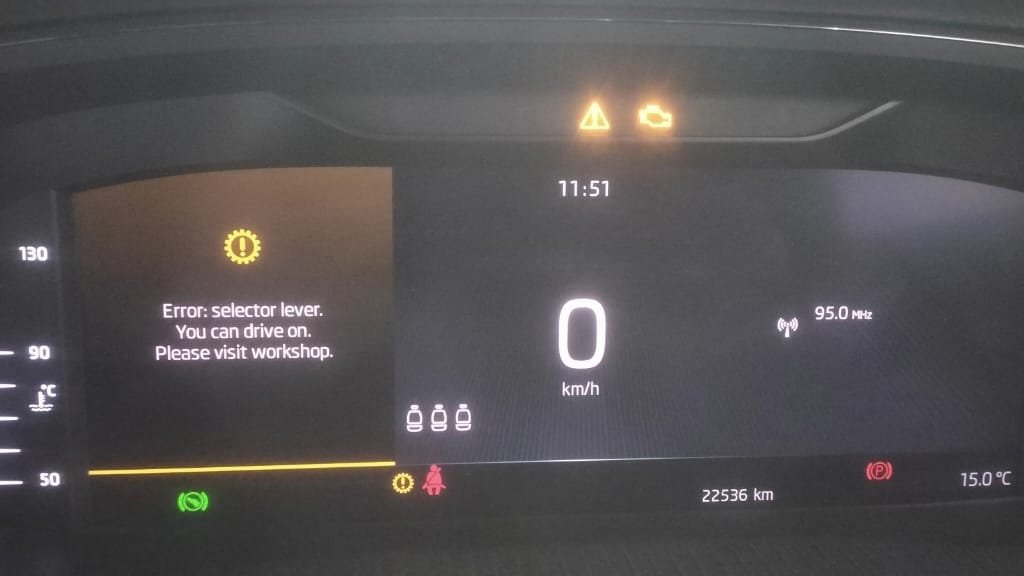
If you’re encountering OBD fault codes like P175D P175E and P177B, it likely points to clutch-related issues in Volkswagen (VW), Skoda, or other VAG group vehicles. The P175E fault code means Clutch 1 Closes Unintentionally, which may lead to poor shifting or transmission malfunction. Similarly, P175D VW or P175D Volkswagen indicates Clutch 1 Opens Unintentionally, affecting power transmission. The P177B VW fault code, also seen as P177B Clutch 1 Tolerance Limit Reached, is a serious warning that could lead to complete clutch failure if ignored. Common in VW P175E, VW P175D, and Skoda P177B vehicles, these errors should not be overlooked. If you’re searching how to fix P175E Clutch 1 Closes Unintentionally, this guide will help you diagnose and resolve the problem effectively. Whether you see P175E VW, P175D VW, P177B, or fault code P175E / P177B, understanding these DTCs is key to maintaining your DSG transmission’s health.
What Does OBD Code P175D Mean?
The P175D code indicates that Clutch 1 opens unintentionally. This fault is intermittent, meaning it doesn’t happen consistently but occurs sporadically. Unintentional opening of Clutch 1 can disrupt power delivery to the wheels, leading to performance issues.
What Does OBD Code P175E Mean?
The P175E code signals that Clutch 1 closes unintentionally. Similar to P175D, this issue is intermittent. Unintended closing of Clutch 1 can cause the vehicle to experience jerky movements or gear engagement at inappropriate times.

What Does OBD Code P177B Mean?
The P177B code indicates that Clutch 1 has reached its tolerance limit, suggesting mechanical wear or a malfunction. This issue may also be intermittent but signals that the clutch is nearing or has exceeded its operational lifespan, requiring immediate attention.
Symptoms of These OBD Codes P175D P175E and P177B
Drivers may notice the following symptoms when these codes are present:
1. Erratic gear engagement: Gears may slip, fail to engage, or engage unexpectedly.
2. Jerking or lurching movements: Especially during acceleration or deceleration.
3. Reduced performance: Power delivery may feel inconsistent or weak.
4. Illuminated Check Engine Light (CEL) or transmission warning light.
5. Transmission overheating: In severe cases, overheating may occur due to clutch slippage.6. Noisy operation: Grinding or whining noises during gear changes.
Common Causes: OBD Codes P175D P175E and P177B Clutch 1
The root causes of these codes typically include:
1. Clutch Wear and Tear: Over time, Clutch 1 may wear out, leading to mechanical malfunctions.
2. Faulty Clutch Actuator: The actuator responsible for engaging and disengaging the clutch may be malfunctioning.
3. Hydraulic Issues: Low hydraulic fluid levels or leaks in the system can impair clutch operation.
4. Transmission Control Module (TCM) Malfunction: The TCM may send incorrect signals to the clutch actuator.
5. Sensor Failures: Sensors monitoring clutch position or operation may provide incorrect data.
6. Electrical Problems: Damaged wiring, corroded connectors, or poor grounding can disrupt the communication between components.
7. Mechanical Damage: Internal transmission components, such as the clutch plate or flywheel, may be damaged or worn out.
How to Diagnose These OBD Codes P175D P175E and P177B
Diagnosing these codes requires a detailed inspection and testing process:
1. Use an OBD-II Scanner: Confirm the codes and check freeze-frame data for insights into when the faults occurred.
2. Inspect the Clutch Mechanism: Check for visible signs of wear, damage, or misalignment in Clutch 1.
3. Test the Actuator: Use diagnostic tools to test the operation of the clutch actuator.
4. Check Hydraulic System: Inspect fluid levels, lines, and cylinders for leaks or contamination.
5. Examine Sensors: Use a multimeter to test clutch position sensors and other related components.
6. Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Look for damaged wires, loose connections, or corrosion.
7. Perform a Mechanical Inspection: If necessary, disassemble the transmission to examine internal components.
How to Fix OBD Codes P175D P175E and P177B
The solutions for these codes depend on the underlying issues:
1. Replace the Clutch: If Clutch 1 is worn or damaged, replace it to restore proper operation.
2. Repair or Replace the Actuator: Address any faults in the clutch actuator to ensure smooth engagement and disengagement.
3. Service the Hydraulic System: Refill or flush hydraulic fluid and repair leaks as needed.
4. Reprogram or Replace the TCM: Update the software or replace the TCM if it is sending incorrect signals.
5. Replace Faulty Sensors: Ensure all sensors related to clutch operation are functioning correctly.
6. Repair Electrical Issues: Fix damaged wiring and secure connections.
7. Inspect and Repair Internal Components: Replace any damaged internal transmission parts, such as the flywheel or pressure plate.
Preventive Maintenance TipsTo avoid similar issues in the future:
1. Regularly Inspect the Clutch System: Monitor for early signs of wear or malfunction.
2. Perform Timely Maintenance: Follow the Conclusion
manufacturer’s schedule for transmission fluid changes and system checks.
3. Avoid Aggressive Driving: Hard starts, abrupt gear changes, and excessive clutch usage can accelerate wear.
4. Address Warning Signs Promptly: Don’t ignore unusual noises, jerking, or performance issues.
Conclusion
OBD codes P175D (Clutch 1 opens unintentionally), P175E (Clutch 1 closes unintentionally), and P177B (Clutch 1 tolerance limit reached) highlight critical issues with Clutch 1 in the transmission system. These faults can affect drivability and lead to costly repairs if not addressed promptly. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and solutions, drivers and technicians can ensure timely resolution and maintain optimal vehicle performance.